Harnessing the power of the sun is crucial for a sustainable energy future.
Solar energy has incredible potential, but its intermittent nature presents a challenge: how do we ensure a consistent power supply to meet our growing energy needs?
This is where solar energy storage comes in. It acts as a bridge between solar generation and consumption, ensuring a reliable source of energy.
In this article, we'll look at the importance of solar energy storage, the advancements in storage technologies, and the impact it has on maximizing the benefits of solar power.
We'll also delve into innovative battery solutions and emerging storage concepts that are shaping the future of solar energy storage.
What Is Solar Energy Storage?
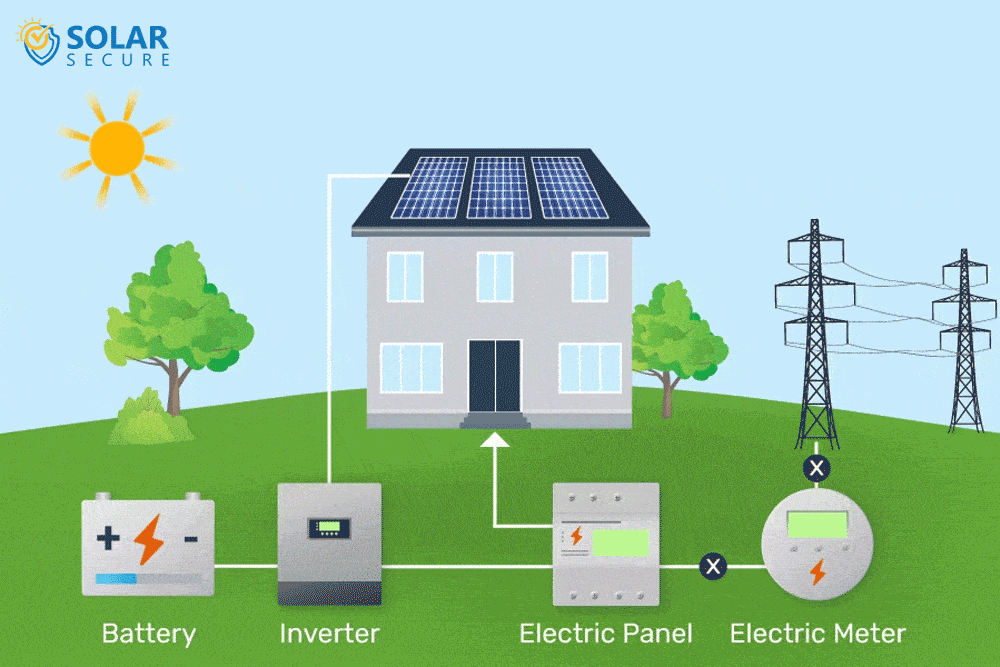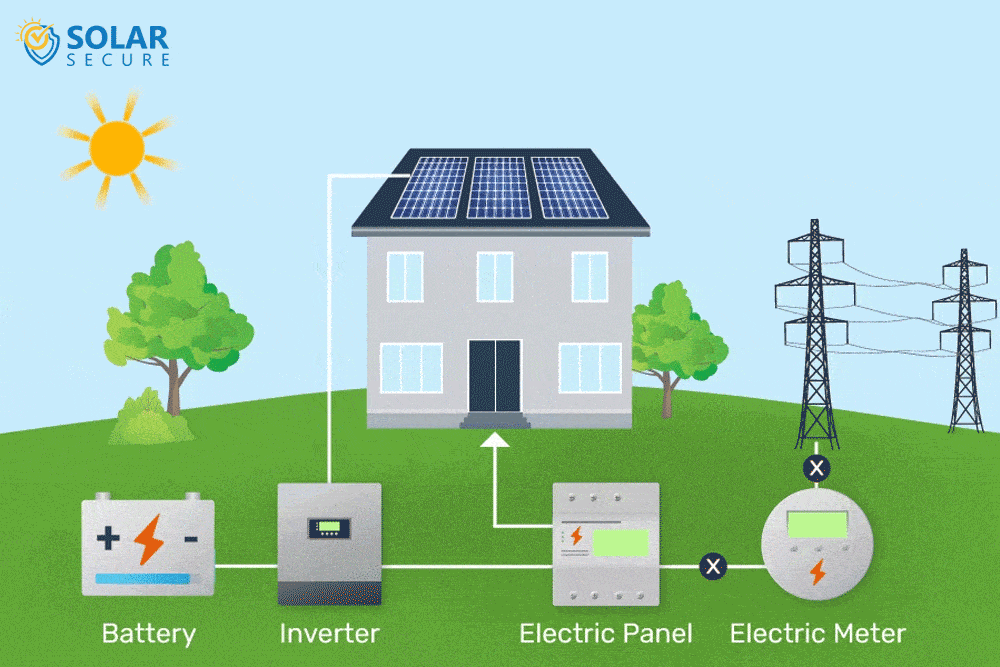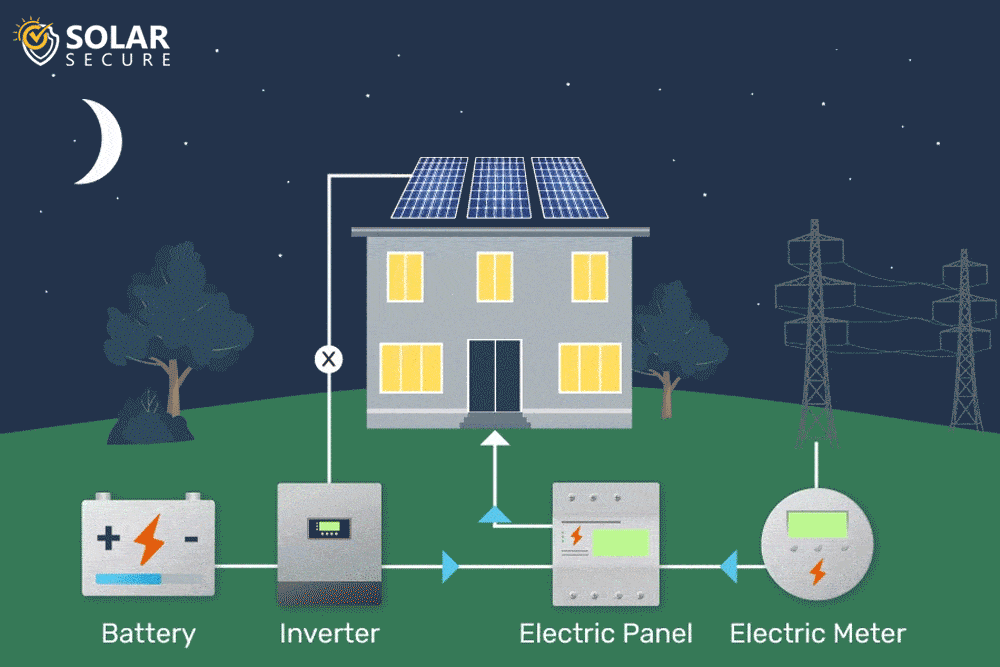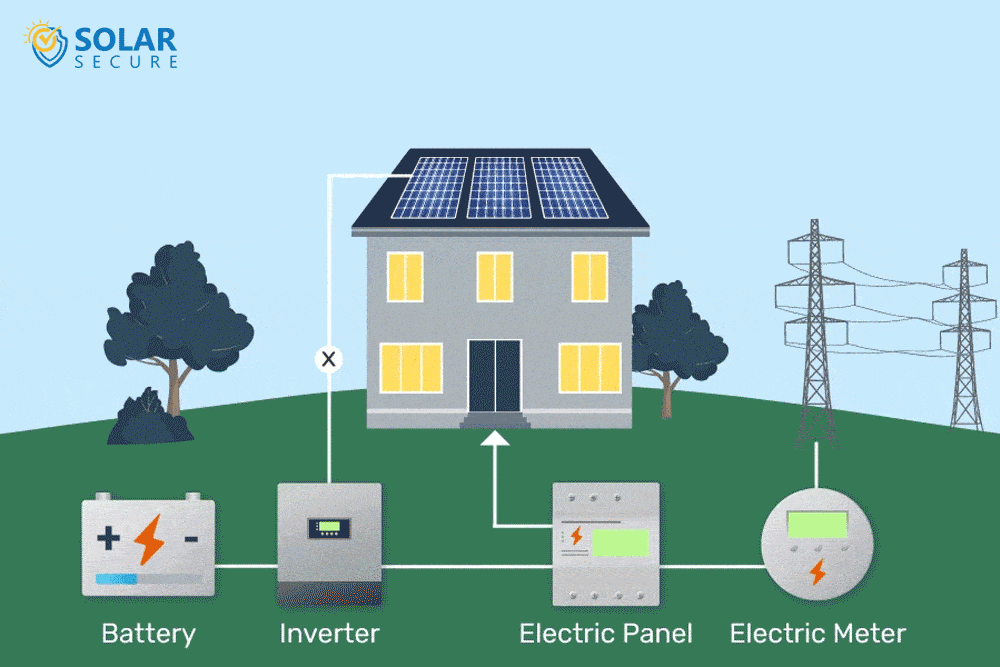
Solar energy storage involves capturing and storing excess energy produced by solar panels for later use when sunlight is limited.
Solar power is generated through photovoltaic (PV) panels, which convert sunlight into electricity. However, solar energy production is intermittent and reliant on weather conditions, resulting in fluctuations throughout the day.
To overcome this challenge and ensure a consistent power supply, solar energy storage systems are utilized.
These systems store the surplus electricity generated during periods of high solar radiation and release it during times when sunlight is scarce or unavailable.
By capturing and retaining extra energy, solar energy storage enhances self-consumption and optimizes the utilization of solar power.
How Is Solar Energy Storage Beneficial?
Solar energy storage offers numerous benefits that enhance the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of solar power systems.
Here are some key advantages:
Increased Energy Independence
Solar energy storage enables individuals and businesses to rely less on the grid by storing excess energy during periods of high solar production.
This greater self-consumption reduces dependence on traditional energy sources, fostering greater energy independence.
Enhanced Energy Reliability
Solar energy storage systems ensure a consistent electricity supply even when sunlight is limited or unavailable.
By storing surplus energy, they mitigate the intermittent nature of solar power generation, providing a reliable power source during cloudy days, nighttime, or power outages.
Time-Shifting of Energy
Solar energy storage allows for flexibility in electricity usage. Excess energy generated during peak solar production can be stored and utilized during times of high energy demand or lower solar power production.
This helps balance energy supply and demand, easing the strain on the grid during peak usage periods.
Grid Support and Stability
Solar energy storage systems contribute to grid stability by smoothing out fluctuations in solar power generation.
They provide a controlled injection of electricity into the grid, helping manage voltage and frequency variations.
This enhances the integration of renewable energy sources, like solar, into existing electricity grids, improving overall grid resilience.
Financial Savings
Solar energy storage optimizes the use of solar power, resulting in potential financial savings.
By storing excess energy during low-demand or lower-rate periods, it can be used to offset electricity costs during high-demand or higher-rate periods. This can lead to reduced overall energy expenses.
Environmental Benefits
Solar energy storage plays a vital role in reducing harmful greenhouse gas emissions.
By maximizing the use of solar-generated electricity, stored energy displaces the need for energy generated from fossil fuels, which release harmful emissions.
This promotes a cleaner and more sustainable energy system, contributing to environmental stewardship.
What Are Our Options In Terms Of Energy Storage Technology Solutions?

There are various types of solar energy storage technologies available for different applications.
Here are some commonly used ones:
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used for solar energy storage due to their high energy density and long lifespan.
They are commonly found in residential and commercial solar energy storage systems as well as in solar generators.
BLUETTI, in particular, uses the latest lithium-ion battery technology in their solar generators, that is, LiFePO4 technology.
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries have been used for solar energy storage for a long time. They are known for their reliability and cost-effectiveness, although they have lower energy density and a shorter lifespan compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Lead-acid batteries are commonly used in off-grid solar systems or areas with unreliable grid connections.
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries store energy in liquid electrolytes held in separate tanks. They offer scalable storage capacity and the potential for long cycle life.
Flow batteries are well-suited for large-scale solar energy storage applications.
Sodium-Based Batteries
Sodium-based batteries, such as sodium-sulfur (NaS) batteries, provide an alternative to lithium-ion batteries.
They offer long cycle life and high energy density, making them suitable for utility-scale solar energy storage systems.
Thermal Energy Storage
Thermal energy storage systems store solar energy in the form of heat. This can be achieved using materials like molten salt or phase-change materials.
The stored heat can be converted back into electricity or used for heating purposes when needed.
Pumped Hydroelectric Storage
Pumped hydroelectric storage is a large-scale energy storage technology that utilizes the gravitational potential energy of water.
Excess solar energy is used to pump water from a lower reservoir to a higher reservoir. When electricity is required, the stored water is released, passing through turbines to generate electricity.
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
CAES systems store excess solar energy by compressing air and storing it underground.
When energy is needed, the compressed air is released, expanding and driving turbines to generate electricity.
Final Thoughts
Solar energy storage has the potential to transform our approach to renewable energy utilization.
As the world embraces a greener and more sustainable future, the focus on developing efficient and cost-effective storage solutions becomes paramount.
Although there are challenges ahead, such as high upfront costs and limited scalability of certain storage technologies, notable advancements have been achieved in recent years.
Lithium-ion batteries, in particular, have revolutionized solar energy storage by expanding their accessibility and practicality across various applications.
Furthermore, emerging technologies such as flow batteries, thermal storage, and innovative concepts like gravity-based systems and compressed air storage offer promising alternatives for addressing large-scale and long-duration storage needs.
Continuous research and development in these fields are driving improvements in efficiency, durability, and affordability.






































































