LED lights have become a ubiquitous lighting solution, preferred by residential and commercial customers alike due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and cost-effectiveness.
LED lights have revolutionized the lighting industry, offering numerous advantages over conventional incandescent bulbs.
In an era where environmental concerns and energy costs are paramount, LED lights have emerged as an eco-friendly and sustainable choice for lighting.
In this article, we'll explore the world of LED lights, highlighting their benefits and applications in various settings.
What Are LED Lights?

LED lights are increasingly popular in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. This is mainly due to their many benefits over traditional lighting technologies.
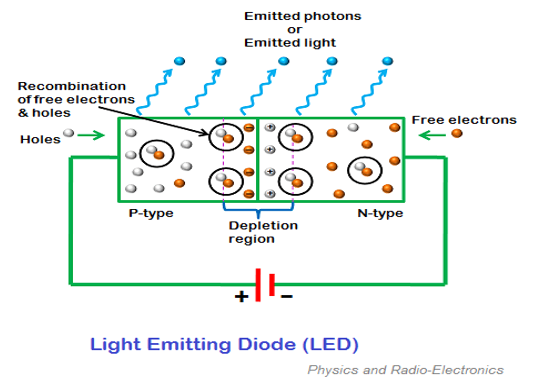
LED lights, which are also known as light-emitting diodes, are a type of lighting technology that use a semiconductor to produce light.
They are often used in many different lighting applications due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and low heat emission.
Essentially, an LED is made up of two parts: a semiconductor material and a positive and negative contact.
When an electric current is applied to the contacts, the electrons in the semiconductor material become excited and begin releasing energy in the form of photons, which is what produces the light.
How Do LED Lights Work?
Below we will give you a step-by-step breakdown on how exactly LED lights work:
- First, a voltage is applied to the LED (Light Emitting Diode) which causes a flow of current through the device.
- The current passes through a semiconductor material (usually a type of solid-state material such as gallium arsenide, gallium nitride, or silicon carbide) in the LED.
- When the current flows through the semiconductor material, it excites the electrons in the material and moves them to higher energy levels.
- As the excited electrons move back to their reduced energy levels, they'll release energy in the form of photons (light particles).
- The photons emitted by the electrons in the semiconductor material determine the color of the light produced by the LED.
- The light produced by the LED then passes through a plastic lens, which focuses the light and determines the beam angle of the LED.
- Unlike incandescent bulbs, LEDs produce very little heat, and the majority of the energy supplied to them is converted into light.
Why Are LED Lights More Energy Efficient Than Incandescent Bulbs?
LED lights are very efficient because they convert most of the energy they consume into light rather than heat.
Traditional incandescent bulbs, for example, emit light as a byproduct of heating a filament until it glows.
This process wastes a lot of energy as heat, resulting in a less efficient use of electricity.
On the other hand, LED lights produce light through a process called electroluminescence, in which a semiconductor material emits photons (light particles) when electrons pass through it.
This process is much more efficient because less energy is needed in order to create the same amount of light.
Additionally, LED lights don't have a filament that can burn out or break, so they have a longer lifespan and require less frequent replacement.
Furthermore, LED lights can be designed to emit light in specific directions. This reduces the amount of wasted light and increases efficiency even further.
In comparison, traditional bulbs emit light in all directions, resulting in a lot of light being wasted by illuminating areas where it is not needed.
Cost Comparisons of LED Lights

The price of LED lights and incandescent bulbs can vary depending on the brand, wattage, and other factors.
Generally, LED lights tend to be more expensive upfront compared to incandescent bulbs, but they are more energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan.
This ultimately leads to significant cost savings in the long run.
For example, a standard 60-watt incandescent bulb can cost around $0.50, while an equivalent LED bulb may cost around $2-3.
However, an LED bulb can last up to 25,000 hours, while an incandescent bulb typically lasts only around 1,000 hours.
So, while LED lights cost more upfront, they are more cost-effective over time due to their energy efficiency and longer lifespan.
Power Comparisons of LED Lights

LED lights use much less power than incandescent bulbs.
For example, a 60-watt incandescent bulb can be replaced by a 9-watt LED bulb, which means the LED bulb uses only 15% of the power that the incandescent bulb uses to produce the same amount of light.
In general, LED bulbs use about 75-80% less power than incandescent bulbs. This translates to significant energy savings over time and lower electricity bills.
How Much Money Can Be Saved Using LED Lights?
The amount of money you'll likely save by installing LED lights in your home is influenced by various factors, including the number of lights you install, your usage frequency, and the cost of electricity in your region.
Research indicates that on average, households in the United States can save approximately $50 to $150 each year by switching from incandescent bulbs to LED lights.
Although at first, it might seem like an insignificant amount of money, it can accumulate considerably over time, particularly if you have numerous lights in your home.
Besides, LED lights have a longer lifespan than incandescent bulbs, implying that you'll save money on replacements.
Final Thoughts
LED lights represent a paradigm shift in lighting technology, as they provide an incredibly efficient and cost-effective lighting solution that offers significant advantages over traditional incandescent bulbs.
LED lights consume much less energy, possess a longer lifespan, emit less heat, and are more environmentally friendly.
While the upfront costs may be higher, the long-term savings in both electricity costs and replacement expenses make them an intelligent choice for both residential and commercial lighting applications.
With ongoing advancements and innovations in LED technology, we can anticipate even greater efficiency, versatility, and affordability in the coming years.