The need for a reliable power source is crucial during blackouts and off-grid trips. Two sources that are commonly considered to serve the purpose are power banks and generators. Both have their set of offerings to align with individual's personal needs.
However, in this technologically advanced era, where every device is built differently, it's essential to understand the key distinctions between these two power solutions to make informed choices.
So, let's tap into the details of these two power resources to understand what can best comply with your needs.
What Is a Power Bank and How Does it Work?
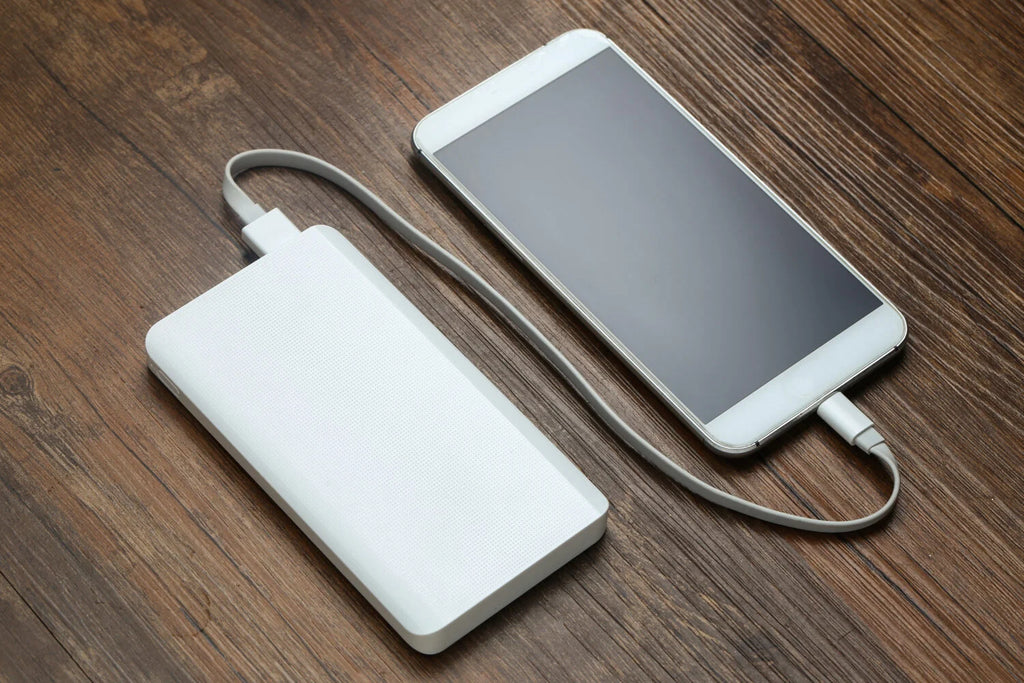

Power banks are small battery-connected devices that have a compact size nearly to fit in a pocket. They are easily portable and integrated with special circuits to balance the flow of current.
Depending on their shape, size, and powering capacity, multiple variables of power banks are available in the markets. Small-size power banks have a capacity of around 20,000 mAh or less as compared to large-sized power banks, which have more extensive capacity offerings than this.
Their working principle is simple and consists of three basic steps that include getting the power, storing it in batteries, and releasing this stored power when required. Firstly, they need to be self-charged through an electrical outlet. Once done, they are ready to supply the current to host devices when required.
What Is a Power Bank Used For?
The use of power banks is becoming a norm with our increasing reliance on tech gadgets. Power banks are commonly used when conventional grid power is not accessible to charge these devices. Depending on the capacity of the power bank, they are compatible with multiple devices.
For example, small-sized power banks have a battery capacity of less than 20000mAh and can support small devices like mobile phones and smartwatches. On the other hand, big power banks come in a power capacity range of 40000-60000mAh and can be used to charge appliances like mini-fridges and laptops.
There are also some variables available in the market that have a battery capacity of around 100,000mAh. However, their reliability is questionable.
Most of the power banks are USB-supported, which means they transfer power through USB ports. However, some of the latest versions also support wireless charging.
What Is a Generator and How Does it Work?
Generators are power backup devices that generate energy by consuming fuels like propane, natural gas, and diesel. These units could be extremely helpful to run your homes and business during power outages.
Talking about the working of the generator, they work on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. To put this simply, they change the mechanical energy produced in the combustion chamber into electrical energy. It mainly consists of 5 parts that are a fuel tank, starter, combustion engine, alternator, and outlets.
As the name shows, the fuel tank stores the fuel, whereas the starter, sometimes assisted with a DC battery, helps start the generator. Then, the fuel is moved to the combustion engine, where mechanical energy is produced and later on converted into electrical energy at the alternator. Lastly, this generated power is supplied to host devices and appliances through outlets.
Types of Generator
There are 4 different types of generators available in the market according to their size and efficiency. Here is a brief guide about all these variables.
- Standalone generators: These are bulky machines that can be used to power entire homes and large-scale industries. They are mostly self-starting units. This means they start automatically when grid power runs out.
- Portable generators: As their name indicates, these types of generators are easy to move. As they are not bulky and big machines, their power output is also low compared to that of standalone generators.
- Inverter generators: These are modern variables of conventional generators. They come with computer chips to supply balanced power and are considered more reliable when the aim is to power voltage-sensitive appliances.
- Induction Generators: These types of generators are not commonly used in households and industries. They require initial mechanical energy to start generating power and production of electromagnetic fields. Their use is most common in wind turbines and mini hydro plants.
Generators are also classified depending on their fuel consumption patterns. Their commonly used types include gasoline generators, natural gas generators, diesel generators, propane generators, solar generators, and biogas generators.
What Is a Generator Used For?
If you are living in an area with frequent power outages, you must be well aware of the importance of generators. These machines are not only helpful during blackouts but also serve as reliable power sources during outdoor camping trips, at construction sites, and in remote locations, to name a few.
To better understand their uses further, here is a comprehensive explanation of generator applications in multiple domains.
Backup Power source
The fundamental use of generators is to provide energy during blackouts. When the conventional grip is inaccessible due to catastrophes like hurricanes, storms, or floods, generators prove to be a viable alternative to grid energy.
Remote construction sites
Generators play a crucial role at construction sites where traditional electricity is not accessible. There are specific generators available that are built to fulfill the energy needs of remote construction sites. Their use case mainly includes powering the machinery, tools, and gadgets necessary for construction activities.
Off-grid parties
An interruptable power supply is crucial to enjoy the full potential of any event. Generators in outdoor venues provide the power necessary to run music systems, lights, food management, and other necessary equipment. Portable generators are most suitable and widely used for such operations.
Power supply in Emergency
Emergency services like fire fighting institutions, hospitals, and police stations need a continuous power supply to run their day-to-day affairs. Generators in such scenarios supply power to life-saving medical equipment, communication, and lighting systems.
Key Differences: Power Bank vs. Generator
Both power banks and generators are built to work as backup power sources. However, depending on their size and output capacity, some key differences distinguish between them.
Supported Appliance
Appliance support is a fundamental difference between a power bank and a generator. Power banks are small devices and come with a limited power storage capacity. They only support small to medium size electronic gadgets.
On the other hand, generators are heavy, bulky machines that vary in size. They are available in small portable sizes to giant machines that can even support the electric load of large-size industries.
Duration of power supply
Power banks supply energy from the stored power in their batteries. They can provide output only when they have power in their batteries. Once their battery power runs out, they need to be charged again to provide electric output.
On the other hand, generators provide electricity by consuming fuels. So, as long as they have fuel in their fuel tank, they can function for hours, days, and even weeks.
Convenience of use
Power banks are small gadgets. Once they are charged, they are ready to use. In the case of generators, they need continuous refueling to keep working. Additionally, they also require periodic maintenance to carry out their functions smoothly.
Portability
Power banks are easily transportable due to their compact size. However, there are some types of generators, like portable generators, that are also easy to move. Still, they are giant machines and require more space for portability as compared to power banks.
Related articles: What Is the Difference Between a Power Bank and a Portable Power Station?
Is a Portable Power Station Better Than a Generator?
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs?
Choosing between a generator and a power station is totally dependent on an individual’s personal requirements. If you need to run multiple medium- and large-size devices, then power stations will be of no use, and you will have to opt for generators.
But in the case of small gadgets, power banks can effortlessly serve the purpose. They are also safer, more reliable, and easier to transport.
Additionally, another factor that counts is the toxicity associated with generators. Whether it is noise pollution or toxic fumes emitted by generators, they are strongly not recommended to be used indoors. In contrast, power banks are sources of clean energy without producing any noise pollution.
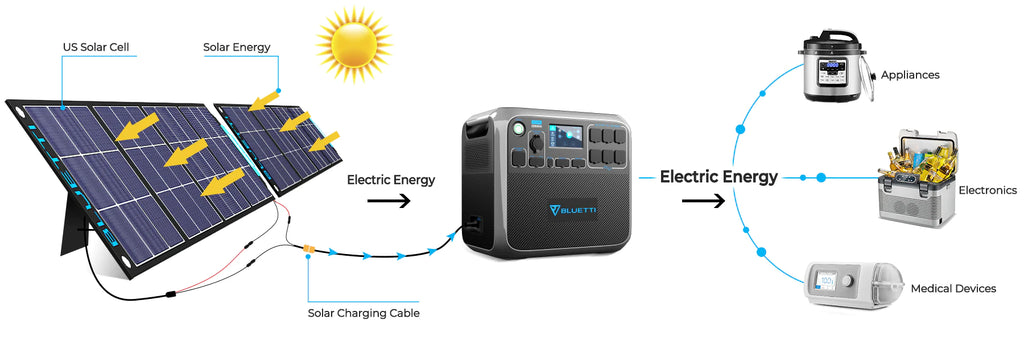
Solar Generators Recommendations from BLUETTI
Generators can effortlessly supply power according to your output needs. However, health concerns caused by the toxic fumes they emit are alarming. Thus, solar generators could be a way to go.
You can explore the BLUETTI official website further to choose any other product according to your needs.
Final Thoughts
Power banks and generators are reliable sources to provide electricity off the grid. Both have some pros and cons associated with them. However, with the advancement in technology, we can expect both products to be soon available with all cons well addressed.
Currently, while opting for any product, it's essential to acknowledge the key differences in their size, capacity, and output. Understand your personal requirements and make a prudent decision by choosing the devices that align best with your personal preferences.




































































